One winter, a client tried to move long timber with a closed trailer. It didn’t work. I suggested a flatbed instead, and they’ve used it ever since.
That quick switch saved them money and time.
I’ve spent years in freight and logistics, helping companies make better transport choices. This advice comes from what I’ve seen, not just what I’ve read.
In this article, you’ll learn what a flatbed trailer is, what makes it useful, and how to know when to use one. It’s everything you need to make a smart decision.
Let’s dive in!
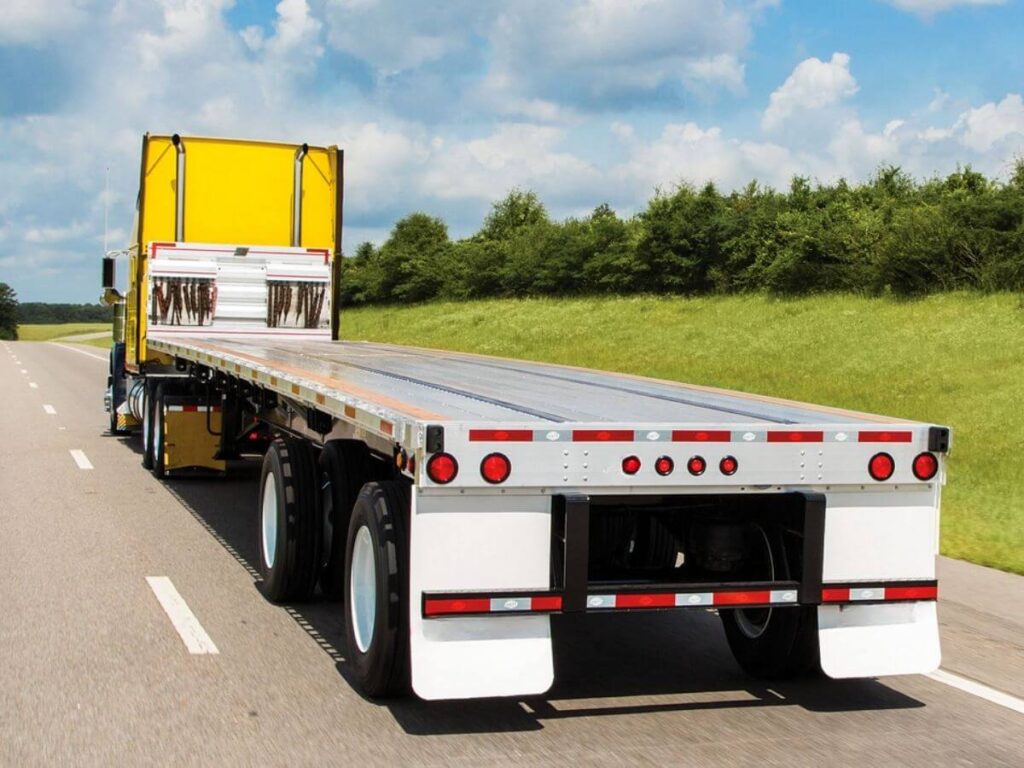
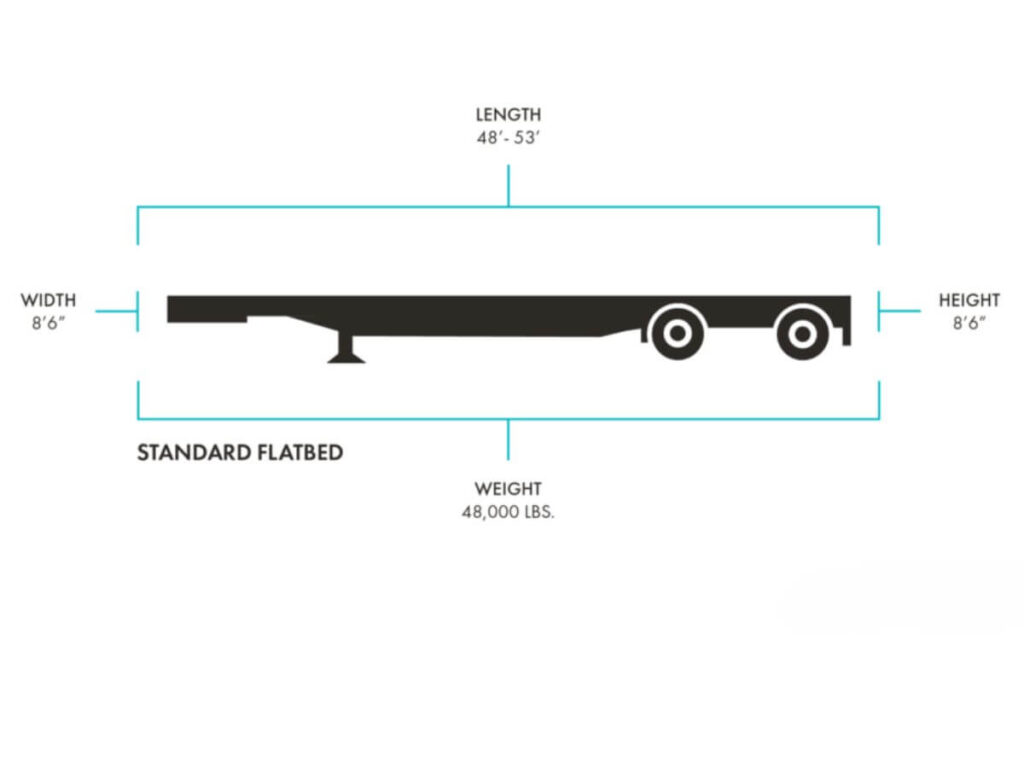
1. What is a Flatbed Trailer?
A flatbed trailer is basically a flat, open platform on wheels. No sides. No roof. Just a heavy-duty surface built to carry loads that don’t fit inside a standard enclosed trailer. That means loading from the top, sides, or back is all fair game. Forklifts, cranes, or even manual setups can be used depending on the site and cargo.
- Works for irregular shapes: When your freight isn’t standard size or shape, like machinery, building materials, or industrial parts, a flatbed trailer gives you the room and access you need.
- Easier loading and unloading: Since there are no walls or doors to work around, teams can load quickly from any direction, saving time and reducing handling headaches.
- Typical size: Most flatbed trailers in the US and many other regions are around 48 feet long and 8.5 feet wide. Some go up to 53 feet for bigger jobs.
- Weight capacity: They usually handle up to 48,000 pounds, which covers a wide range of industrial freight needs.

2. Advantages of Using a Flatbed Trailer
There’s a reason flatbed trailers show up again and again across different industries. They’re not just easy to recognize, they’re built to solve real problems in everyday freight operations.
Easy Loading and Unloading
One of the best parts of using a flatbed trailer is how easy it is to load and unload. With no walls or roof to work around, forklifts and cranes can access the cargo from any side. This speeds things up on busy job sites where time is money. It also reduces the risk of damage during awkward maneuvers inside tight trailers. Even in less-than-ideal conditions, flatbeds make loading straightforward and less stressful for your crew.
Hauls Oversized or Irregular Cargo
Flatbeds don’t care if your load is tall, wide, or just plain awkward. You can stack, strap, and position items that wouldn’t fit in a closed trailer. That makes them ideal for construction materials, machinery, and other bulky freight. When standard trailers fall short, flatbeds step in without skipping a beat. It’s a practical solution for hauling loads that don’t follow the rules.
Versatile Across Industries
From agriculture to manufacturing to energy, flatbeds are everywhere. That kind of versatility means you can repurpose your fleet instead of buying niche trailers for every job. Businesses love having one trailer that works across projects. It keeps logistics simple and operations lean. Whether it’s pipes today or pallets tomorrow, a flatbed can usually handle both.
Reduces Downtime and Increases Efficiency
Because flatbeds are quicker to load and can carry larger or weirder shapes, they help keep delivery schedules tight. Fewer delays at the dock means less downtime on the road. They also reduce the need for disassembly or repacking, which saves labor and time. In the end, that adds up to real cost savings across the board. It’s the kind of quiet efficiency that shows up in your bottom line over time.

3. Types of Flatbed Trailers
Not every flatbed trailer is built the same, and that’s a good thing. Depending on what you’re hauling, the wrong trailer can slow down the job or even lead to fines. The right one, on the other hand, makes loading easier and keeps your cargo safe. It helps to know your options before making a decision.
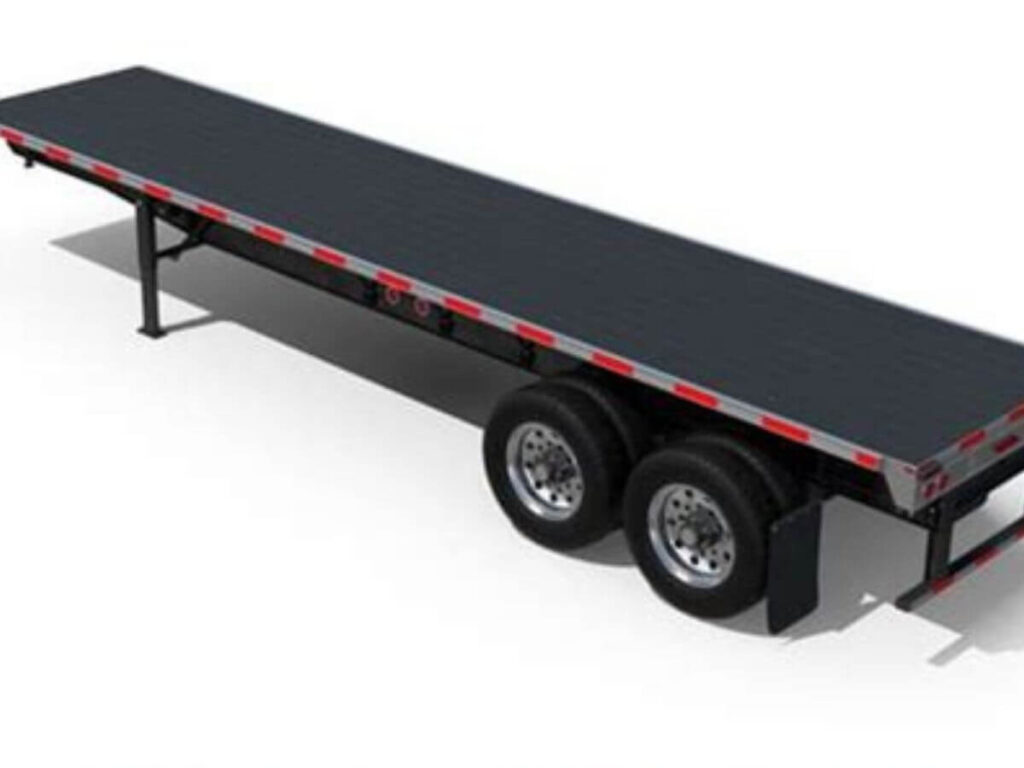
- Standard Flatbed Trailer: It has a flat, open deck with no sides or roof, making it ideal for general freight, pallets, and construction materials. If your cargo doesn’t need extra clearance or special handling, this one usually gets the job done.

- Step Deck (Drop Deck) Trailer: A step deck has two levels, with a lower deck in the rear to allow for taller cargo. It helps you avoid height restrictions without switching trailer types. Many use it for taller equipment or materials that need to sit lower to the ground.
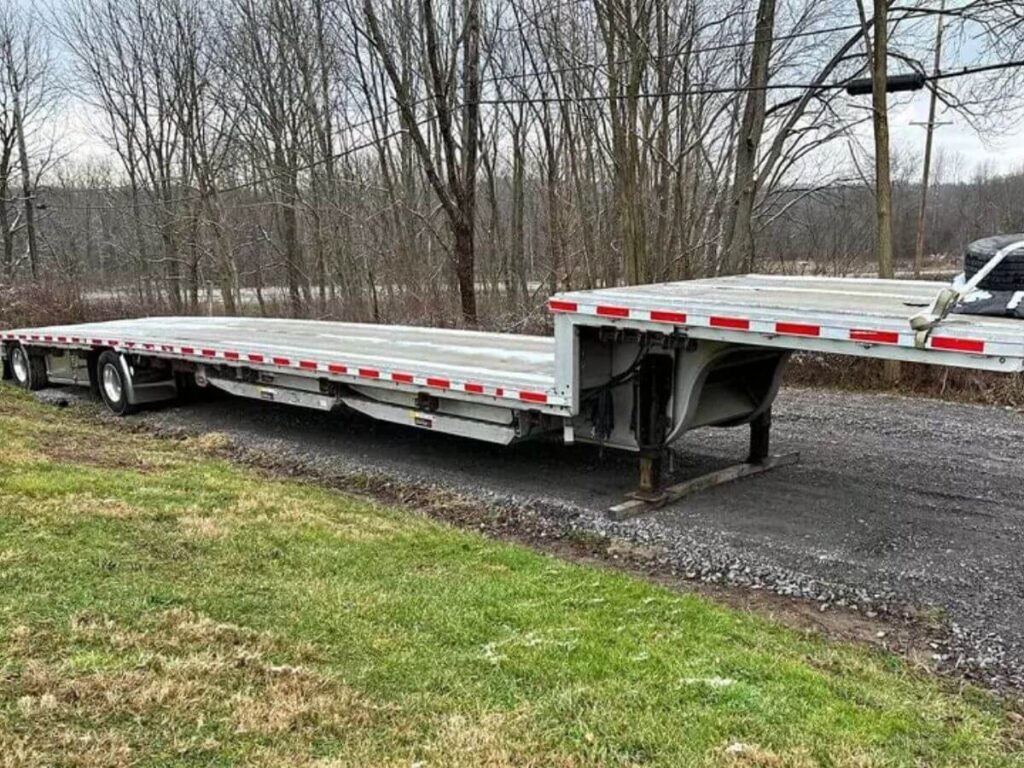

- Double Drop Trailer: This trailer has a low center deck that sits even lower than a step deck. It’s used for moving tall items like heavy machinery or industrial tanks. The design keeps your load legal in height while giving you extra clearance.
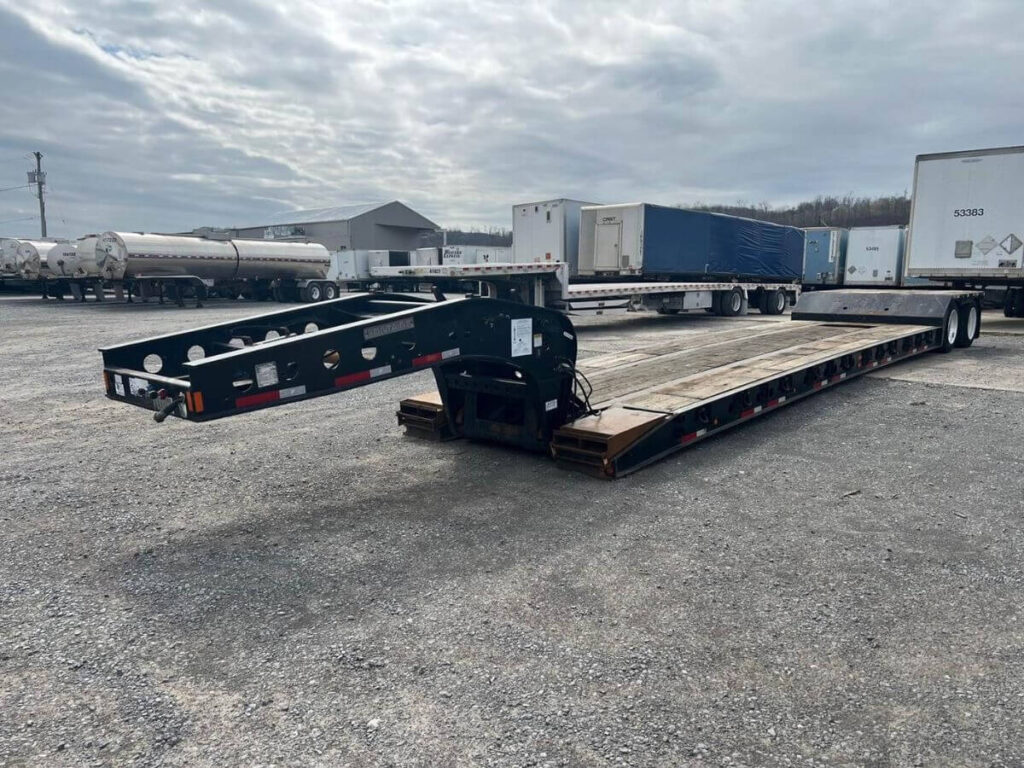

- Extendable Flatbed Trailer: When your cargo is longer than a standard flatbed can handle, this one extends to match the job. It works well for steel beams, windmill parts, or long pipe sections. You can adjust it to suit whatever length you’re dealing with.
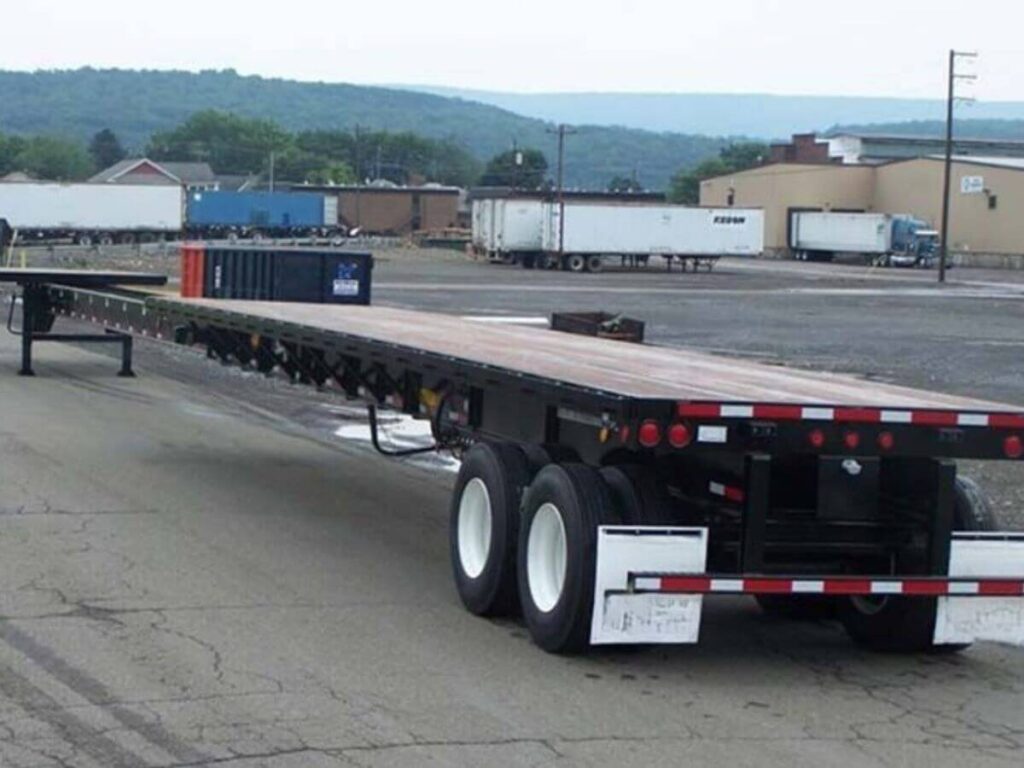

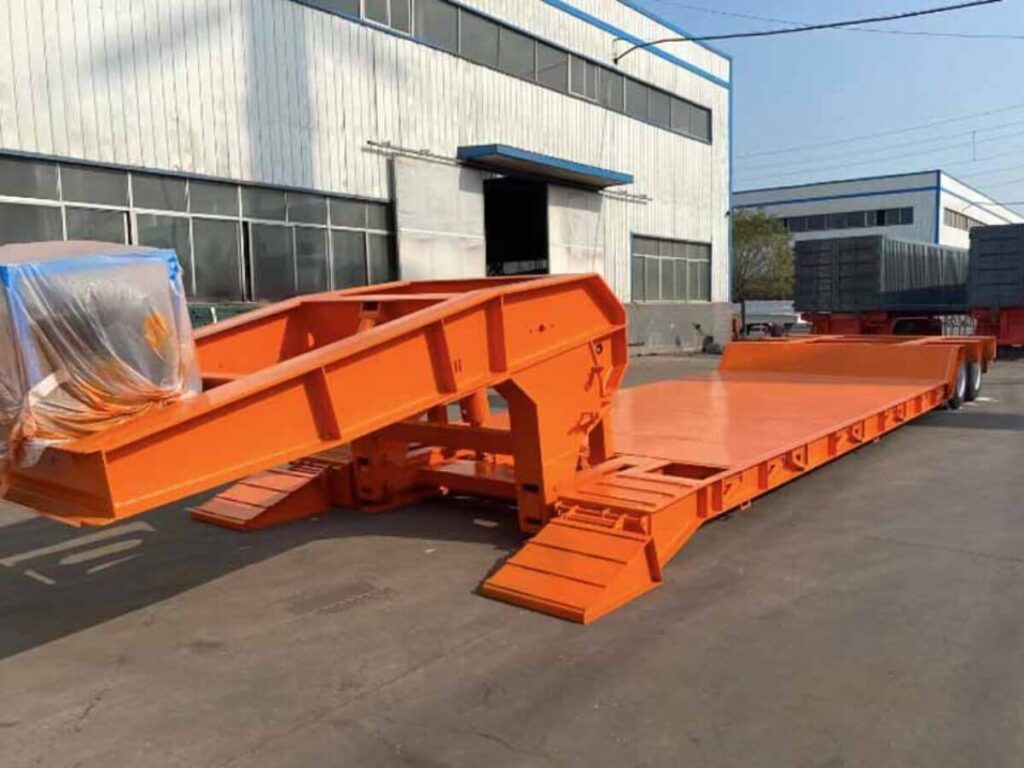
- Removable Gooseneck (RGN) Trailer: The front of this trailer detaches to let equipment be driven or rolled right onto the deck. It’s a solid choice for moving dozers, excavators, or anything that can’t be lifted easily. These are built for serious hauling, especially when weight and loading method are both concerns.

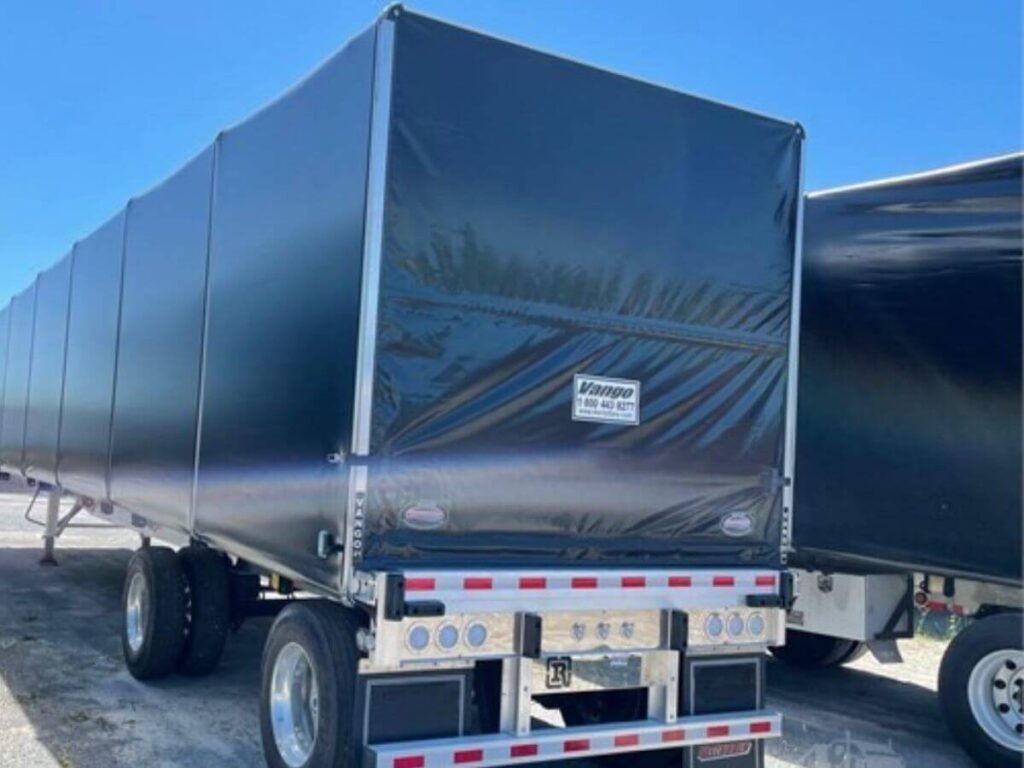
- Conestoga Flatbed Trailer: This trailer looks like a standard flatbed but comes with a sliding tarp system that protects your cargo. It gives you weather protection without losing the flexibility of open loading. Great for loads that can’t get wet but also can’t fit in an enclosed trailer.

4. Common Features and Specifications
Before you pick a flatbed trailer, it helps to understand the basic features they all tend to share. These small details often make a big difference out on the road or at the job site.
- Deck Length: Most flatbed trailers are 48 feet long, but some stretch to 53 feet for extra capacity. The right length depends on the size and type of cargo you move most often.
- Deck Width: Standard width is usually 8.5 feet, which fits within legal road limits in most regions. It gives enough space for wide loads without needing special permits.
- Maximum Weight Capacity: Flatbed trailers typically handle up to 48,000 pounds. If your loads are heavier, you’ll want to look into specialized models like RGNs.
- Material and Build: Most decks are made from steel, aluminum, or a mix of both. Steel offers strength, while aluminum keeps the trailer lighter for fuel efficiency.
- Tire and Axle Configuration: Tandem axles are common for stability and weight distribution. Some models include spread axles to reduce wear and better handle uneven loads.
- Load Securement Options: Flatbeds usually come with multiple stake pockets, D-rings, and winches for straps. These give you flexible ways to tie down different cargo types.
- Floor Surface: The deck surface can be smooth or feature friction patterns for grip. A textured surface helps prevent shifting when loads aren’t perfectly balanced.
- Lights and Reflectors: All flatbeds are equipped with DOT-approved lighting and reflective tape. This improves visibility and safety during night driving or poor weather.
5. Common Uses and Industries
Flatbed trailers show up in more places than most people realize. Their open design makes them a go-to option for all kinds of businesses moving big, heavy, or awkward items.
Construction and Building Materials
The construction industry relies heavily on flatbed trailers for moving materials like lumber, steel beams, concrete forms, and scaffolding. These items are often long or bulky, and a flatbed makes it easier to load and unload them directly at job sites. Since construction schedules are tight, quick access to materials can keep projects on track. A flatbed helps crews get what they need without unnecessary delays.
Manufacturing and Industrial Equipment
Manufacturers often ship large equipment or machine parts that are too wide or tall for enclosed trailers. Flatbeds allow easier transport of generators, tanks, or fabricated structures. These loads usually require cranes or forklifts, and flatbeds make that process much smoother. When you’re dealing with freight that cannot be broken down or boxed up, flatbeds give you the room to work with.
Agriculture and Farming
Agricultural businesses often move heavy machinery, hay bales, feed, and irrigation equipment over long distances. Flatbed trailers offer the flexibility needed for different types of farm cargo. They also make seasonal moves faster, especially during planting or harvest time. In rural areas where space is open but timing is critical, flatbeds make a real difference.
6. Buying vs. Renting a Flatbed Trailer
Deciding whether to buy or rent a flatbed trailer depends on how often you use it and what kind of jobs you handle. Here’s a clear side-by-side breakdown to help you weigh both options.
| Factor | Buying a Flatbed Trailer | Renting a Flatbed Trailer |
| Upfront Cost | High initial investment, but no recurring rental fees. | Lower upfront cost, typically paid per day, week, or job. |
| Long-Term Value | Can save money over time if used frequently. | More expensive in the long run if rented often. |
| Maintenance | You are responsible for all repairs and regular upkeep. | Maintenance is often covered by the rental company. |
| Flexibility | Less flexible if your needs change or cargo types vary. | You can choose the trailer type that fits the specific job each time. |
| Availability | Always available when you own it. | May not be available on short notice during busy seasons. |
| Depreciation | Value drops over time and may affect resale. | No concern about depreciation or resale. |
| Customization | You can modify or equip it to match your hauling needs. | Rentals are standard and may not have all the features you prefer. |
| Storage Needs | You’ll need space to store it when not in use. | No storage required once it’s returned. |
| Cash Flow Impact | Affects capital and budgeting more heavily upfront. | Easier to manage within short-term budgets. |
| Usage Frequency | Ideal for regular or high-volume hauling. | Better for occasional or seasonal use. |
7. Factors to Consider When Buying Flatbed Traile
Buying a flatbed trailer is a serious investment, and the wrong choice can cost you down the line. It helps to slow down and focus on the details that really matter for your business.
Load Type and Size
Start by thinking about what you’ll be hauling most often. If your loads are long, heavy, or oversized, you’ll need a trailer that can handle the weight and dimensions safely. Some cargo needs extra length, while others may require a reinforced deck. Matching the trailer to your regular load type prevents costly problems later.
Material and Build Quality
Not all flatbeds are built the same, and materials play a big role in performance. Steel trailers are stronger but heavier, while aluminum versions offer better fuel efficiency with less strength. Some models combine both to balance weight and durability. It’s worth checking weld quality, flooring, and frame design before buying.
Legal Requirements and Permits
Weight limits, trailer dimensions, and safety features all need to meet regional transport regulations. If your trailer is too tall or wide, you could face fines or need special permits. It’s smart to research local laws before finalizing your purchase. Staying compliant helps avoid delays and unexpected costs during delivery.
Long-Term Operating Costs
The purchase price is just one part of the total cost. You’ll also need to factor in maintenance, tire replacement, insurance, and potential repairs. A lower-priced trailer might cost more in the long run if it breaks down frequently. Look for models known for reliability and lower upkeep over time.

Conclusion
That winter delivery I helped fix with a flatbed trailer? It saved the project, the budget, and the client.
Now you know what a flatbed trailer is, what it’s built for, and how it fits into different industries.
Whether you buy or rent, care for it or customize it, every section in this guide gives you the clarity you need.
If you’ve got freight that doesn’t fit the mold, why wait?
Contact us today at Rhinotrail and get expert support that moves your business forward.


